EFL · National City (Australia) Framework presentation
- Basic framework section
1, Framework section: Country elements
Australian National Flag

Signature Construction: The Sydney Opera House, Australia

[Country Name] The Australian Federation (The Commonwealth of Australia).
[area] 7.692 million square kilometers.
[population] 25.69 million (September 2020). 74% are British and Irish, 5% Asian, 2.7% indigenous, and 18.3% of other peoples. The official language is English, and Chinese is the second most spoken language except English. About 63.9% of the residents believe in Christianity, and 5.9% believe in Buddhism, Islam, Hindu and other other religions. The unreligious or unknown population 30.2%.
[Capital] Canberra (Canberra).
[Head of State] Queen Elizabeth II. The Governor represented the Queen for a five-year term. The current Governor, David Hurley, was sworn in on July 1,2019.
[Important Festival] Australia Day (Australia Day): January 26th.
[Brief], located between the South Pacific and the Indian Ocean, consists of islands like mainland Australia, Tasmania and overseas territories. The Coral Sea and the Tasman Sea near the Pacific Ocean, the north, the west and the south face the Indian Ocean and its marginal seas. The coastline is 36,735 km long. The north is tropical and mostly temperate. The annual average air temperature is 27 ℃ to the north and 14 ℃ to the south.
The earliest residents were the indigenous people. In 1770 British navigator James Cook arrived on the east coast and declared British possession of the land. The first group of British prisoners exiled to Australia on 26 January 1788 arrived at Sydney Bay, and England began establishing colonies in Australia, which was later designated Australian Day. In July 1900, the British Parliament passed the "Constitution of the Commonwealth of Australia" and "the Dominion Ordinance of Britain". On 1 January 1901, the Australian colonial districts were changed to states, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. It became an independent country within the Commonwealth in 1931. In 1986, the British Parliament passed the "Relations Act with Australia", and Australia was granted full legislative power and judicial final adjudication.
[Parliament] The Australian Federal Parliament was formed in 1901, consisting of the Queen (represented by the Governor of Australia), the House of Representatives and the Senate. The parliament adopts a universal vote.
[Government] The federal government consists of a House majority or coalition of parties, with the party leader serving as prime minister and the ministers appointed by the premier. The government term is generally 3 years.
[Administrative divisions] The country is divided into six states and 2 districts. The six states are New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, Western Australia, Tasmania, and the Northern Territory and the Capital Region.
[Judiciary] The Federal High Court is the highest judiciary in Australia with appellate jurisdiction over other courts at all levels and making decisions on cases involving constitutional interpretation, consisting of one Chief Justice and six justices.
[Party] Major Australian political parties are: (1) The Liberal Party (Liberal Party) (2) The National Party (National Party) (3) Other small Australian Labor Party parties are the Green Party, the Single National Party and the Communist Party of Australia.
[Economy] Australia is an industrialized country with developed agriculture and animal husbandry, rich natural resources, rich in sheep, cattle, wheat and sucrose, and is also an important producer and exporter of mineral products in the world.Agriculture, animal husbandry and mining industries are traditional industries in Australia, manufacturing and high-tech industries develop rapidly, and the service industry has become the leading industry of the national economy. Since the 1970 s, a series of economic reforms have been carried out, vigorously developing foreign trade and maintaining rapid economic growth. Between 1991 and 2008, the average annual economic growth rate was of 3.5%, ranking among the top among OECD countries. In recent years, economic growth has slowed as international commodity prices declined, the Australian mining boom subsided, and public fiscal pressure rose. Affected by the COVID-19 epidemic and 2020, the economy showed negative growth in fiscal 2019 / 2020. However, Australia's financial system is stable, with strict supervision, and has a large room for macroeconomic policy adjustment, which is better than other western countries in the international financial crisis.
Since the 1980 s, Australia has achieved rapid growth through effective economic restructuring and reforms, achieving a series of longest continuous growth in developed economies. In 2019, the Australian GDP reached A $ 195 million, an increase of 2.2%. A per capita GDP of $ 76,000 per capita, is one of the rapidly growing developed countries in the world. Influenced to the COVID-19 outbreak, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) expects Australia's economic growth to drop 6.7% in 2020.
Australian economy in the last five years

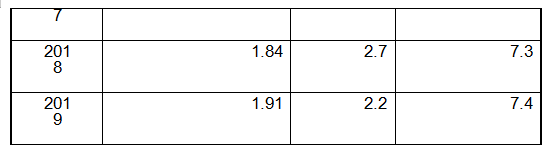
Source: The Australian Bureau of Statistics
Main economic data are as follows:
GDP (FY 2019 / 2020): A $ 195 million.
Economic Growth (FY 19 / 20): -0.2%.
GDP per capita (FY 2019 / 2020): about A $ 76,000.
Currency: Australian dollar ($ 1 ≈ $ 0.77, March 2021).
Unemployment rate: 5.8% (February 2021).
Exchange reserves: A $ 54.8 billion (January 2021).
[Resources] It is rich in mineral resources, with at least 70 species. Among them, the proven economic reserves of lead, nickel, silver, uranium, zinc and tantalum rank first in the world. Australia is the world's largest producer of lithium and zirconium, and the output of gold, iron ore, coal, lithium, manganese ore, nickel, silver, uranium and zinc also ranks the top in the world. Australia is also the world's largest exporter of bituminous coal, bauxite, diamond, zinc concentrate, the second largest exporter of alumina, iron ore and uranium, and the third largest exporter of aluminum and gold. The proven mineral reserves with economic mining value include about 5.3 billion tons of bauxite, 14.6 billion tons of iron ore, 40.3 billion tons of black coal, 30 billion tons of lignite coal, 22.9 million tons of lead, 22.6 million tons of nickel, 41,400 tons of silver, 40,835 tons of tantalum, 41 million tons of zinc and 5570 tons of gold. Crude oil reserves are 227 billion litres, and natural gas reserves are 2.2 trillion cubic meters. Forest coverage is 21% and the natural forest area is about 163 million hectares (2 / 3 is eucalyptus).It is rich in fishery resources, and the fishing area is 16% more than the land area. It is the third largest fishing area in the world. There are more than 3000 kinds of seawater and freshwater fish and more than 3000 kinds of crustacean and software aquatic products, among which about 600 species have been carried out for commercial fishing. The main aquatic products are prawns, lobster, abalone, tuna, scallops, oysters, etc.
[Industries] mainly manufacturing, construction and mining. In FY 18 / 19, construction produced A $ 146.13 billion. Manufacturing output was A $ 109.979 billion. Mining output value: A $ 185.754 billion.
[Agriculture and animal husbandry] Developed agriculture and animal husbandry, plays an important position in the national economy, is the world's largest wool and beef exporter. In FY 2018 / 2019, Australian agricultural and animal husbandry output was A $ 40.605 billion. The main crops are wheat, barley, cotton, sorghum, and the main livestock products are beef, milk, mutton, wool, poultry, etc.
[Foreign Trade] In 2019, Australian trade in goods maintained a weak growth. According to Australian statistics, the import and export of trade in goods was US $ 486.09 billion, up by 0.4% from the same period last year (the same below). Of these, exports were US $ 272.27 billion, up 5.9%; imports were US $ 213.82 billion, down 5.8%. The trade surplus was $ 58.45 billion, up 94.3%. .
In 2019, Australia's top five trading partners were China, Japan, the United States, South Korea and Singapore. Among them, the top five Australian exporters were: China ($ 103.902 billion), Japan ($ 39.769 billion), South Korea ($ 17.479 billion), India ($ 10.49.226 billion), United States ($ 10.273 billion); the top 5 import sources were: China ($ 55.068 billion), America ($ 25.007 billion), Japan ($ 14.951 billion), Thailand (A $ 10.327 billion) and Germany ($ 10.186 billion).
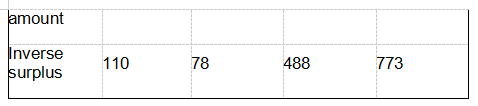
See it by country (region), In 2019, Australian exports to China, Japan, South Korea and the United Kingdom accounted for 38.2%, 14.6%, 6.4% and 3.9% of the total Australian exports, respectively, For $ 103.90 billion, $ 39.77 billion, $ 17.48 billion, and $ 10.49 billion, Exports to China and the UK increased by 18.3% and 188.1%, respectively, Exports to Japan and South Korea fell by 3.8% and 1.2%, respectively, Exports to the above four countries account for 63% of the total Australian exports; Imports from China, the United States, Japan, and Thailand represent 25.8%, 11.7%, 7.0%, and 4.8% of the total Australian imports, respectively, For $ 55.07 billion, $ 25.01 billion, $ 14.95 billion, and $ 10.33 billion, Imports from the US increased by 7.2%, Imports from China, Japan and Thailand fell by 0.8%, 11.2%, and 7.4%, respectively. The top five sources of surplus in Australia are China, Japan, South Korea, India, and the UK, with $ 48.83 billion, $ 24.82 billion, $ 9,11 billion, $ 6.66 billion and $ 5.48 billion, mainly from the US, Germany, $ 8,09 billion, and $ 7.23 billion, respectively, down 120%, 8.0% and 15.1% for the United States and Thailand.
[Trade Structure]] Australia is an important exporter of primary products in the world, and the export of finished products, high-tech products and services has also been growing rapidly. The main export products of the Australian goods trade are mineral products, agricultural products, including iron ore, coal, hot air, wheat, beef, wool and cotton; the main imported commodities include mechanical and electrical products, transportation equipment, chemical products and so on.
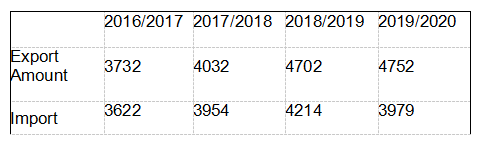
By commodities, mineral products, precious metals and products and animal products are the main exports of Australia. In 2019,62.6%, 6.4% and 5.8% of total Australian exports respectively, US $ 169.78 billion, $ 18.02 billion and $ 18.88 billion, increasing 10.9%, 11.8% and 8.5% respectively. Plant exports of another major export product fell 15.9%, reducing their share of exports to sixth. In addition, the exports of chemical products and base metal products have also declined. Mechanical and electrical products, transportation equipment and mining products are the top three categories of goods imported by Australia, with a total import of 113.71 billion US dollars in 2019, accounting for 53.2% of the total Australian imports. Imports of major imports in Australia declined, including mineral imports by 11.6%, imports of base metals and products by 11.7%, and imports of transport equipment by 7.9%, pushing overall imports to 6.0%. Australia is more dependent on international trade. Australia's main trading partners are China, Japan, the United States, South Korea, Singapore, New Zealand, Great Britain, India, Malaysia, Thailand, Germany, etc. The import and export of commodity and services trade in recent years is as follows (in A $ 100 million):
Major Australian exports are iron ore, coal, education and travel services, gold, crude oil, natural gas, wheat, bauxite, copper mines, beef, copper, wool products, etc. The main imported commodities are crude oil, motorcycles, refined oil, aviation equipment, drugs, communication equipment, computers, buses, trucks, gold, etc.
[Trade Policy] Australia implements the market diversification strategy, and the priority areas of trade policy are: domestic reform, committed to the single window management of international trade, actively promote export, support the multilateral trade system, and actively carry out bilateral and regional free trade agreement negotiations. Currently, the Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) has been approved by the Australian Parliament and officially entered into force on 30 December 2018; the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) has concluded negotiations in November 2019, which is expected to be signed in 2020.
The China-Australia trade dates back to the late 19th century. Since the establishment of diplomatic ties in 1972, the economic exchanges and cooperation between the two countries have been continuously strengthened. In recent years, China and Australia have had close economic and trade cooperation exchanges and frequent interaction. In 2003, the two countries signed the Trade and Economic Framework for China and Australia, and decided to carry out a joint feasibility study on the free trade zone and promote bilateral cooperation in mining, agriculture, service, investment and other fields. In 2005, the two countries launched negotiations on the China-Australia Free Trade Agreement. On 17 November 2014, the two governments jointly confirmed the substantive conclusion of the negotiations. On 17 June 2015, the two countries officially signed the Free Trade Agreement between the Government of the People's Republic of China and the Australian Government, and the 20 December 2015 agreement officially had 36 effects to Australia. In March 2017, the Chinese and Australian governments signed the Statement of Intent to Review the Relevant Contents of the China-Australia Free Trade Agreement, officially announcing the launch of the bilateral FTA Services Section, the Investment Section and the Memorandum of Understanding on the Investment Facilitation Arrangement in 2017. In October 2017, the two sides carried out the first round of deliberations on the China and Australia Free Trade Agreement. The China-Australia Free Trade Agreement is the first time that China has negotiated a free trade agreement with major developed economies with a large economy. It is also one of the highest overall level of trade and investment liberalization signed by China and other countries so far. In the field of service trade, Australia is the first country to make a commitment to trade in services to China on a negative list. The Investment Facilitation Arrangement is the first special facilitation arrangement made by developed countries for projects and technicians under China's investment projects. Australia is the second country in the world to negotiate a holiday visa arrangement and professionals with Chinese characteristics, giving China up to 5,000 work vacation visas every year and a developed country with the largest number of access to China. The Australian and Hong Kong Free Trade Agreement came into force in January 2020. Under the agreement, the import and export of goods will achieve zero tariffs, service providers will get market access, and two-way investment conditions will be significantly improved.
The China-Australia Ministerial Economic Committee mechanism was formally established in 1986,
It is held every two years, and is held in turns in the two countries. In September 2017, the 15th China-Australia Ministerial Economic Committee was held in Beijing, with Minister of Commerce Zhong Shan and Australian Minister of Trade, Tourism and Investment Qiao Bo presiding.
In 2019, China continued to be Australia's largest trading partner, the largest export destination and the largest source of import.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the bilateral trade volume between China and Australia was US $ 158.97 billion in 2019, up 10.9%. Among them, Australia's exports to China were US $ 103.90 billion, up 18.3%, accounting for 38.2% of total Australian exports, up 4.0 percentage points; Australia imported from China US $ 55.07 billion, down 0.8%, or 25.8% of total Australian imports, up 1.4 percentage points. Australia's trade surplus with China was US $ 48.83 billion, up 51.1 per cent.
Mineral products mainly metal sand have always been the main export product of Australia to China. In 2019, exports was USD 71.39 billion, an increase of 29.0%, accounting for 68.7% of the total Australian exports to China. Animal products are the second largest category of Australian exports to China, with US $ 4.18 billion, up 47.3%, or 4.0% of the total Australian exports to China. Textiles and raw materials are the third largest category of goods exported to China, with US $ 2.50 billion, up 4.0%, accounting for 2.4% of total Australian exports to China. As the share of mineral products in exports to China is nearly 70%, the performance of mineral exports to China basically determines the overall performance of Australian exports to China, while the rapid growth of animal products and textiles and raw materials further increases the growth of Australian exports to China. China was one of Australia's fastest-growing major export markets in 2019, second only to the UK.
The main commodities imported from China are mechanical and electrical products, textiles and furniture and miscellaneous products. The total products imported US $ 33.71 billion in 2019, accounting for 61.2% of the total Australian imports from China. In addition to the above products, base metals and products, plastic rubber, mineral products are also the major commodities (Class HS) imported by Australia from Australia 37, China, accounting for more than or nearly 5% of their imports. In general, Australia from China imports, in sharp contrast to the continuous high growth rate of Chinese exports, which also makes Australia 's trade surplus to continue rapid growth, growth as high as 51.1%, China is the largest source of Australian trade surplus, Australia' s surplus accounted for more than 80% of the surplus, bilateral trade imbalance continues.
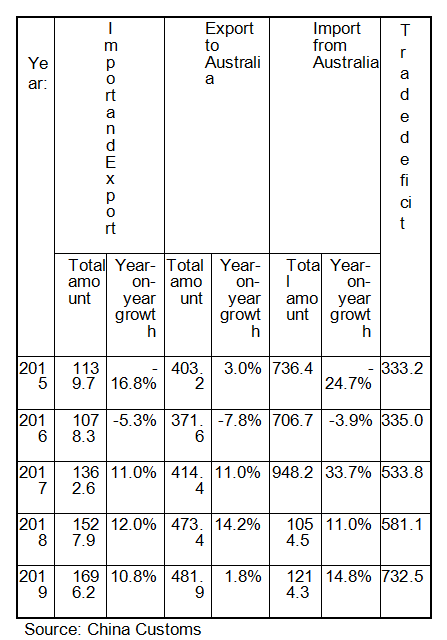
According to Chinese customs statistics, in 2019, the bilateral trade between China and Australia was US $ 169.62 billion, up 10.8% year on year, of which China exported to Australia US $ 48.19 billion, 1.8% year on year, USD 121.43 billion, up 14.8% year on year, and the trade deficit against Australia was US $ 73.25 billion.
Statistics Table of Goods Trade in Australia in the Recent Five Years
(In the unit: USD 100 billion)
China and Australia has made breakthroughs in service trade. According to Australian statistics, the total bilateral service import and export in FY 2018 / 19 was nearly A $ 22 billion, up by 8% year on year, including Australia's service export to China increased by 8.2%, representing 19% of total Australian service exports; Australian service imports from China increased by 7%, accounting for 3.4% of total Australian service exports. China is Australia's second largest service trading partner and the largest service export market. In 2019, the number of Chinese visitors to Australia reached 1.43 million and reached A $ 12.4 billion, the largest source of tourists in Australia. In 2018, gross Australian education exports reached A $ 35.8 billion, up 16.3% year-on-year. China accounts for 33.2%, marking Australia's largest education export market, growing 16.9% year-on-year. India represented 13%, the second largest market, up 33.3% Yo.
Since the implementation of the China-Australia Free Trade Agreement, the dividends have been continuously released. According to the Chinese customs, in 2019, the bilateral import and export volume between China and Australia reached USD 169.64 billion, increasing by 10.8%. China has become Australia 's largest trading partner, export market and source of import for 11 consecutive years, and Australia is China' s seventh largest trading partner. According to Australian statistics, the total bilateral service import and export in FY 2018 / 19 was nearly A $ 22 billion, up by 8% year on year, including Australia's service export to China increased by 8.2%, representing 19% of the total Australian service exports; Australian service imports from China increased by 7%, accounting for 3.4% of the total Australian service import. China is Australia's second largest service trading partner and the largest service export market. In 2019, the number of Chinese visitors to Australia reached 1.43 million and reached A $ 12.4 billion, the largest source of tourists in Australia. Australia is also one of the main destinations for China's foreign investment. According to statistics from China, by the end of 2019, Chinese direct investment in Australia has US $ 40.39 billion, and Australia is the sixth largest direct investment destination in China. According to Australian statistics, by the end of 2019, China 's direct investment stock of A $ 46 billion in Australia, up by 10% from the end of last year, is Australia' s fifth largest source of direct investment.
Australian Culture
[Culture] Australian culture is known for its diversity. Aboriginal painting and music, Western traditions and modern art, and Asia-Pacific culture have imperceptibly influenced Australia and flourished on the land. Australian films often win awards at World Film Festivals and deliver a lot of great talent to Hollywood. The Sydney Opera House is the palace of Australian art, and its completion also laid the foundation for the Australian cultural export. It is Patrick White, the giant of modernist literature, who plays a pivotal role in the internationalization of Australian literature.
Australians love sports and especially Australian style rugby. As a world sports power, a number of major international events are held here all the year round. Australians are also in love with art, and visit galleries or watch art shows almost twice as many as football. Annual 70% of Australians line up to watch movies, book fans spend about A $ 1 billion a year on buying books, about 25% of Australians watch at least one opera a year, and about 20% of Australians patronize the galleries.
Thanks to this multicultural culture based on social harmony, equality and cultural identity, Australia's domestic political situation is basically stable and social security is generally good. Historically, Australians have been strengthened by the Australian social principles, and generally have a very strong faith and attitude.
Traditionally, the immigrant mix since the founding of the Australians has strengthened their distrust of dignitaries. So until now, the Australians still believe that their society is an egalitarian society. This values and belief are reflected in the Eureka fence incident and the deeds of the Green Forest respectively. To this day, this values and faith are still manifested in high poppy syndrome.
About whether there is Australian culture, Australians have two different views: a think that Australia has no unique culture, everywhere is foreign books, music, painting, and film and television works, and local work is just these foreign culture imitation and derivative, after all, Australian culture (modern) history only more than a hundred years. Australians's attitude towards the UK is quite complicated. Many people have cultural inferiority in the UK and even other European countries and feel that everything in Europe is better than the local things in Australia. But as Australia has increased contact with the rest of the world, the awareness has faded.
Literature and Art
Australian contemporary art is as unique and diverse as the society and the continent from which they come from. They not only reflect the ancient style of the birthplace of the world's oldest and continuous cultural traditions, but also show the traditions of the rich source of immigrant cultural sources.
Aboriginal and non-indigenous artists responded to the fantasy challenges posed by Australia and created new ways to express their art and culture, attracting the attention of the international community.
All forms of performing arts including music, drama and dance have a warm following in Australia. In recent years, Australian performing arts has reached new standards in both skill and quality.
Australia has produced a large number of poets and novelists, making Australian literature one of the most important components of contemporary English literature. Like Henry Lawson, Banjo, Petterson, Hope, Christina Tina Steade and the Queen's Poetry Gold Award First Australian winner Judith White. The Australian film industry has achieved such an outstanding international reputation, thanks to Australian writers. Spielberg 's box office blockbuster, Schindler' s List, pted Thomas Kennelly 's Booker Award-winning novel Schindler' s Ark, while Australian writers are at the lead in using new media such as the Internet and multimedia.
2, Framework: News hotspot
(1) Note! This popular food in Australia contains a lot of E. coli! Health authorities issued an emergency recall notice, IGA supermarkets, food stores are available-sohu network
https://m.sohu.com/a/243321891_222390? _trans_=010004_pcwzy
(2) Wine News! Australian wine exports fell 29% to Chinese mainland last year
https://www.jiemian.com/article/5643481.html
(3) Australian media say that Australian food and agriculture and other fields have become new hot spots in China's investment
http://finance.china.com.cn/industry/20150204/2945825.shtml
(4) The consequences against China are very serious! Australia was hit again and important commodities suddenly into focus
https://xw.qq.com/cmsid/20210331A02GSJ00? f=newdc
3, Framework Section: National · Human Geography
Australia, occupying the Australian continent, surrounded by the sea, the Pacific Ocean, and the northwest three facing the Indian Ocean. Northern Australia is only about 500 km from the Asian country of East Timor. New Zealand, belonging to Oceania, faces Australia across the Tasman Sea, about 1,500 km from Australia's east coast.
From 1605, the Dutch boarded part of the Australian coast, after which the British and French followed. In 1770, British James Cook sailed far to the Pacific, landed on the eastern south bank of Australia and held the land under the name King George III, named New South Wales. Formal colonization began in 1788, and it was designated Australia in 1817.
Australia is the smallest continent in the world, located in the southern hemisphere, with a total area of 7.692 million square kilometers, ranking sixth in the world. The Australian coastline is 36,735 km, surrounded by water on all sides, so its enchanting ocean beauty, world-famous sun beaches and colorful coral colonies attract many tourists from all over the world every year.(Source: Baidu encyclopedia)
- Natural View of East Coast Australia-EAST COAST-Australia-Chapter #3 https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=uy1pa6nlTT0
(2) Travel promotional shorts: Melbourne, Australia-Melbourne-Welcome to travel https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=VuORJHzRf2c
(3) Most Beautiful Natural View Sydney Australia Watsons Bay to Circular Quay hiking Love Holy Land
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1HW41117Fb? share_source=copy_web
(4) Sydney | Next stop Paradise
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xt411c7As? share_source=copy_web
- Frame Section: Latest Information
(1) Food Safety Management https://www.docin.com/p-1475334497.html in Australia
(3) Food Standards Code Australia on Chinese Food Safety Legislation https://xuewen.cnki.net/CJFD-SZFG200603010.html
(4) Chinese Food Violation of Australian Imported Food Control Law in 2020 http://news.foodmate.net/2021/02/584329.html
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/7b24f249be1e650e52ea9935.html
- [Food Safety Law of the People's Republic of China] Australian immigrants earning ability competition! Irish group lead
http://www.dgssmy.com/huaren/2021022556978.html
- Australian Revised Australian New Food Code
http://www.hunansp.com/biaozhunfagui/78287.html
- Australia proposes to amend nutritional and new resource food regulations in the New Food Standards Code
http://www.cankaowuzhi.com/article/149976
- Australia asked: Why can China give some reasons to reject Australian beef imports?
https://www.163.com/dy/article/FCK85SBS0543AUG0.html
(10) Original | ANZ Irradiated Food Regulatory System http://law.foodmate.net/show-205069.html
- Professional framework section
5, Framework Section: National · Food Introduction
[Agriculture and Animal husbandry] Agriculture and animal husbandry, is Australia 's traditional advantageous industry. The production and export of agricultural and animal husbandry products occupy an important position in the national economy. Australia is one of the world' s leading exporters of 23 wool and beef. In FY 2018 / 19, gross agricultural output increased by 3% to A $ 60.4 billion. In 2019, Australia exported $ 2.672 billion of beef to China; 4.087 billion, 1.28 billion of wine, 1.06 billion; 700 of lobster and 2 million tons of barley. As of 30 June 2019, the number of agricultural entities has decreased by 4% to 89,400 compared with the previous year, and the area of agricultural land has increased by 2% to 384 million hectares year-on-last-year.
China's exports to Australia rose 11.2%, according to G. G. last year
China Net, January 14 (reporter Peng Yao) Today, the State Information Office held a press conference. Li Kuiwen, spokesman of the General Administration of Customs and director of the Department of Statistics and Analysis, introduced that in 2020, the total import and export value of China and Australia was 1.17 trillion yuan, down by 0.1%. Of these, exports to Australia were RMB 370.23 billion yuan, up by 11.2%; imports from Australia were RMB 796.35 billion, a decrease of 4.6%. In terms of major trade commodities, China's main export commodities exported to Australia in 2020 are mechanical and electrical products and labor-intensive products, accounting for 76.1% of the export value. The main commodities imported from Australia are mainly iron ore, natural gas, etc., accounting for 70.6% of the import value.
http://au.mofcom.gov.cn/article/ddfg/haiguan/202102/20210203040389.shtml
6, Framework Section: Food Standards [State Market Regulatory Administration]
7, Framework Section: Policy and Regulations [State Administration for Market Regulation]
7.1 What are the regulations and policies on foreign trade?
7.1.1 Trade Authority
The Australian department is the Ministry of Foreign Trade (Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade), mainly responsible for developing trade policy, making trade advice to the government and conducting international negotiations to expand international space for Australia's economic development. The Customs authority is the Ministry of Internal Affairs (Department of Home Affairs).
7.1.2 Trade Legal System
Major trade-related laws are the Customs Law, Competition and Consumer Law, Company Law, Bankruptcy Law, Trademark Law, Copyright Law, Patent Law and so on.
Relevant Provisions for 7.1.3 Trade Management
The Australian government has certain control measures for both the import and export of goods, in violation of these regulations, will be subject to severe sanctions by the government.
[Import management] The management form is divided into absolute prohibition and restriction. There are absolutely prohibited products, including dogs (dangerous varieties), human embryo genes and suicide devices. Restricted imports include certain animals, marine organisms and plants and their products, commodities potentially harmful to health (including chemicals and radioactive substances), certain items related to cultural heritage, such as cultural relics, commodities that need quarantine, substances that cause ozone holes, weapons, drugs, narcotics and anabolic substances that may cause mental damage; Antibiotics; Goods with ANZAC patterns; Asbestos, Cat and dog fur products; Ceramic glaze products; Whale products; Chemical weapons; chewing of tobacco and snuff; Cosmetics containing harmful substances; Fake credit cards; Equipment for controlling the crowded personnel; Cultural heritage from Papua New Guinea; Diamond; Dog collars; Drugs and narcotics; Dangerous species (animals and plants); Clearval; Explosives and plastic bombs; Guns and ammunition; Electronic mosquito and fly beats, with certain official symbolic patterns (such as the national emblem), and designed commodities; human or animal growth hormone; HFCs Incandescent Light; Cava medicine; A Knife and a dagger; Radadium radiation indicator; Toxic substances; Subthat destroy the ozone layer; Pencils and coatings containing harmful substances; Pesticides and other hazardous chemicals; Polychlorinated polyphenbenzene, Tribenzene and polyphenols; Porn goods; Radiosubstances; Sensitive chemicals such as ammonium nitrate; Tabpress; Articles used for medical treatment; unprocessed tobacco; Toys containing toxic substances; Arms of goods for war, etc. Specific provisions Yes, Yes Parameter See the Australia Large Leigh: Asia: Inside the Service Department Network Station: ( www. homeaffairs.gov.au/Busi/Impo/Proh#). Moreover, in order to prevent the plague, to prevent diseases and pests
Injury, environmental protection, temporary industries, and the implementation of international agreements may also impose temporary and phased import restrictions.
[Export Restrictions] The Australian Government controls certain export goods, divided into absolute ban and export restrictions. There are two types of prohibited products: suicide devices and anhydrous acetic acid. The 21 categories of products such as red wine, brandy, narcotics and human embryonic genes are goods that restrict export. Specific provisions
See the Australian Ministry of the Interior website (www. homeaffairs.gov.au/Busi/Expo/Proh).
7.1.4 Import and Export Commodity Inspection and Quarantine
Australia has a strict and conservative quarantine system, and is recognized as one of the countries with the strictest global animal and plant inspection and quarantine measures. It not only effectively protects its domestic biosafety, but also restricts the entry of foreign animal and plant products and protects the domestic agricultural products market to the maximum extent. The competent authorities for the inspection and quarantine of imported products are the Australian Biological Safety Bureau and the Inspection and Quarantine Bureau.
Under the meat and livestock industry export license regulations, the meat and livestock industry Act, the meat and livestock industry regulations, the Livestock Export Standards and the Export Animal Control Order, Australia implements an export license management system for domestic meat and livestock.
[Import Risk Analysis System] The Australian biosafety Bureau conducts an import risk analysis of foreign animal and plant products applied to enter Australia, confirming that the risk level is acceptable to import by the recipient. Australia also implements an import licensing system for animal and plant products, most of which must also be imported after obtaining import permits. Only imports of animal genetic material —— semen (cattle, cats, deer, dogs, giraffe, sheep, horses, rats) and embryos, cattle, sheep, sheep, rats) are allowed from the state approved by the Australian Ministry of Agriculture.
According to this plan, foreign animal and plant food entering Australia should not only pass import risk analysis, but also meet the requirements of the Import Food Control Law in quarantine. The Australian Inspection and Quarantine Bureau has divided imported food into three categories according to safety: risk food, active supervision food and sampling supervision food, and taken different inspection measures from strict inspection to sampling inspection. In addition, the relevant provisions are: poultry, eggs need to be imported through strict inspection and has no high pathogenic avian flu certificate, the seedlings, fresh cut flowers and other corrosive air cargo to check before inspection and quarantine of the packaging. The Australian Ministry of Agriculture modified the import conditions of fresh cut flowers and green plants in March 2018, previously allowing methyl bromine fumigation after goods arrived in Australia, and now requires pest control measures before export shipments and reduced biosafety risks in production, packaging and maritime transportation.
7.1.5 Customs Management Rules and Regulations
[Management System] The Customs Act in 1901, which was amended in July 1999 and May 2005. Under the Customs Act, the Australian Government imposes duties and goods and services duties on most of the imported goods.
[Import Tariff] The tariff rate of import tariff depends on many factors, such as the type of goods and origin, and the applicable tax rate of most goods is between 0% and 5%. Higher tariff rates apply to certain commodities such as alcoholic beverages, tobacco, textiles, clothing, and footwear. Generally, import tariffs can be divided into special tax rates and general tax rates. Special tax rates include tariffs on the island countries below the South Pacific; zero tariffs on the least developed countries and East Timor; and tariffs below general but above those in the developing countries and regions. In addition, the corresponding tax exemption or preferential tax rates shall be granted according to the bilateral trade agreements or free trade agreements signed between Australia and the relevant countries. The general tax rates apply to all other countries and regions and to imports in tariff tables without special preferences but under special tariff rates. The Australian government has also implemented a tariff reduction system through the customs. The China-Australia Free Trade Agreement came into force in December 2015 and began the first tax cuts. According to the agreement, after the tax reduction transition period, Australia 's tariffs to China' s products have been reduced to zero, and China's tariffs on most products in Australia have been reduced to zero. The China-Australia Free Trade Agreement establishes a timetable for reduction commitments on Chinese imported goods, as see:
dfat.gov.au/trade/agreements/in-force/chafta/official-documents/Do cuments/chafta-annex-i-tariff-schedule-of-australia.pdf
Import Commodity Rate Import import Rate
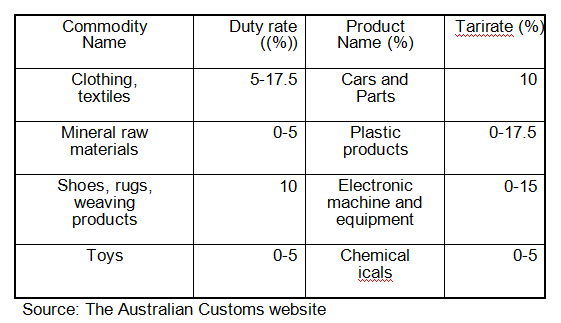
[Tax payable] Generally speaking, the tariff value of imported goods as the tax basis and implements ad valorem collection. The calculation formula is: = customs value * applicable tax rate.
[Export Tax] Australia exports uranium to export tax and no export tax on other products. Australia has implemented an export tax rebate system. Upon the export of imported products, we may require a refund of import duties and consumption taxes. Tax rebates may be granted for exporting new unused imported products, or finished products containing imported products components, or imported products used for processing. Finproducts indirectly contain imported ingredients (e. g. oil) will not be refundable.
(1) Australia issues Australian New Food Code Amendment No 167
http://law.foodmate.net/show-190008.html
http://news.cnnb.com.cn/system/2017/04/10/008622258.shtml
8, Framework Section: Exhibition Exhibition (Food)
(1) 2021 Australia International Food Show FINE FOOD_ Outreach Network
http://www.yshows.cn/zhanhui/470.shtml
Basic Information
Name: Australia International Food Show 2021 FINE FOOD
Name: FINE FOOD
Exhibition Date: September 00,2021-00,09,2021
Exhibition Venue: Sydney, Australia
Exhibition cycle: 2 years and 1 session
Sponsor: Diversified Exhibitions Australia
Organization: Beijing Zhongling International Exhibition Co., Ltd.
Industry properties
Food, Beverage, Wine, and Tobacco
Exhibit exhibits
1) Food Service, Catering Equipment: baked food, blenders, cabinets, kitchen utensils, dishwasher, dishwashers, kitchen refrigeration equipment, frying pan, ice maker, oven, packaging equipment, packaging technology, etc.;
2) Food and Beverage: baked goods, coffee, pastries and candy, dairy products, drinks, food preservation devices, food materials and additives, meat, organic food, sauces, seafood, aquatic products, etc.; retail catering equipment, etc.
Exhibition introduction
The Australian Food Show (Fine Food) is one of the important exhibition projects hosted by Diversified Exhibition Company Australia, a member of the Exhibition Association of Australia, and this exhibition is a UFI registered project, supported by the Australian Government Trade Council. Founded in 1994, the show gathers the latest food, beverage products, and related equipment. As the largest food industry activity in the country, it has attracted many buyers from the retail and catering industries, and expanded new channels and businesses for all those who participated in the exhibition.
Market Background
The number of Australian food imports from China is rising year by year. Total Australian imports from China rose rapidly, rising from $ 133 million in 2000 to $ 2.7 billion in 2005, with $ 280 million in exports and $ 2.41 billion in imports. Both countries have a broader space for development in strengthening agricultural cooperation and promoting trade in agricultural products. According to the Australian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Australia imports seafood and semi-finished products from China first, and second is cereal processed food. China is also a major supplier of processed vegetables, preserves and fruit juice in Australia. Industry insiders in the food industry say that most food processing procedures in Australia contain ingredients from China.
http://www.onezh.com/haiwai/index_59918.html
Exhibition: 9 September-12 September 2019 (4 days from Monday to Thursday)
Exhibition cycle: once a year
Exhibition Country: Sydney
[Exhibition Introduction]
Exhibition content:
1) agricultural and sideline products, canned food, leisure food, meat, aquatic products, condiments, soy products;
2) Convenient food, grain and oil products, frozen food, dehydrated vegetables, edible fungi, green food, freeze-dried food;
3) health food, infant food, poultry products, dairy products, dried fruits and vegetables, baked food;
4) drinks, coffee, tobacco, alcohol, biscuits, candy, food ingredients and additives, tea and local products, etc.;
5) Food Processing Technology, Food Machinery, ice cream production technology, packaging technology.
Exhibition introduction:
Australia International Food, Beverage and Hotel Supplies Exhibition is an international trade show for retailers and the food and catering industry, the largest international food show and one of Australia's largest food industry events. The show (Fine Food Australia), hosted by Diversified Exhibition Australia, brings together the latest food, beverage products and related equipment worldwide and is the largest exhibition in the field of the Australian food industry. The exhibition is sponsored by a member of the Australian Exhibition Association, and the exhibition is an International Exhibition Union (UFI) certified program, supported by the Australian Government Trade Council. The show is held annually, alternating in the cities of Sydney and Melbourne. Australia International Food and Beverage and Hotel Supplies Show, featuring the latest food, beverage and processing machinery from around the world. Every year, the exhibition attracts food and beverage producers and trading professionals from all over the world. It is an ideal exhibition for China's food enterprises to negotiate trade, transactions and exchanges to Australia, New Zealand and even the world. The exhibition strictly controls visitors and ensuring the opportunity to interview exhibitors with more real buyers.
9, Framework Section: Food Category
General situation of seafood products:
Australia has more than 60,000 kilometers of coastline, a wide region, polarized climate, pure and pollution-free natural environment to create an excellent quality of Australian seafood. Australian seafood is known for its low yield and high value, including the Australian dragon, the Australian abalone and the famous bluefin tuna.
Seafood Product Policy:
Imports of raw shrimp and shrimp, suspended on 6 January 2017 due to the prawn white spot syndrome virus (WSSV), will be lifted on the July 6, according to a G/SPS/N/AUS/422/Add.1 circular released by Australia. It is worth noting that after the lifting of the ban, the Australian authorities required all imported shrimp and shrimp products in accordance with the latest quarantine inspection regulations, will be all products strictly tested to ensure product safety, the relevant export enterprises should pay high attention to and timely response measures.
Export situation to China:
Since 2013, direct trade in China has grown, especially last year, as exports jumped from A $ 85 million (EUR 54.3 million / US $ 64.4 million) to A $ 358 million (228.7 million / EUR 28.77 billion). The product widely sold in the Chinese market is abalone, the second highest valued seafood in Australia, with exports of A $ 182 million (Euro 116.3 million / $ 1135 million from 2015-2016).
- Framework section: Brand recommendation
Famous seafood brand:
Western John, Simplu Group, kailis Family, kbseafoods, kailisbros, nationalfisheries, Kelis Brothers
- Framework section: Enterprise recommendation
Famous seafood company:
JOHN WEST(Western John)
Founded in 1857, JOHN WEST(West John) is one of the most popular Australian seafood brands, with a profound history of hundreds and a hundred years of brand history. Since his birth, John West JOHN WEST() has been adhering to the spirit of exploration and exploration, fishing high-quality fresh seafood in rough waters. It is also because of this unparalleled enthusiasm and dream, JOHN WEST(Western John) adhere to technological innovation in maintaining the flavor of fresh fish, constantly improve the methods and eating methods of fishing wild fish, always adhere to bringing high quality fresh seafood to people's tables, won the reputation of "seafood expert", around the world.
The kailis Family
Established in 1926, Kailis Bros, after decades of operation and expansion, has developed from originally a Perth retail fish store to a well-known seafood supplier and exporter in Western Australia. According to the FY 2014-15 operating report, Kailis Bros had annual operating income of A $ 435 million (RMB 2.127 million), total assets of A $ 109 million (RMB 534 million), annual net profit rose 80% to A $ 13.3 million (RMB 65.185 million) and annual annual dividend of A $ 8.5 million. Kailis Bros, a subsidiary of KB Seafoods, provides more than 6,500 seafood and affiliated products to mainstream supermarkets and catering enterprises in Australia, and also exports high-end products such as lobster to the East Asian market, with the main brands including KB's, By George, Clipper K, etc.
Kelis Brothers, Inc.
Kelis Brothers mainly specializes in seafood retail, wholesale and aquaculture, and has continuously invested in tropical reef rock lobster and slippers and lobster breeding research for several years. At present, a series of technologies have been successfully developed from lobster seedling breeding to cultivation. In 2007, Kelis Brothers established the Lobster Qingfeng Company, which is committed to commercialize the research results of lobster breeding technology and establish an innovative model of commercial breeding. It is understood that the company is the only company in the world that can be from reef rock lobster incubation to cultivation, and one of the three companies in the world can complete the slippers lobster from incubation to the formation.
http: / / au.mofcom.gov.cn / article / catalog/ddqy / 202103 / 20210303043522.shtml
III. Professional Data
- Framework section: National · Food Data
(1) Overview of China-Australia Bilateral Trade in 2019
https://www.baidu.com/link? url=pi8Nii2hDbS5aTz7ZTxWDXY4OrKOpXPBeixRJtv0FrGPMV9NHiXyWxrr9vx-oSmOzZAe4-8T-xVytdLaYhf5ZpF0b97ZMbMXukduksmx7fC&wd= & eqid=fb04f7c80001b4930000000560993eb3
(2) China backhand, Australia lost money, trade minister to sit back with China
https://new.qq.com/omn/20210508/20210508A06ONU00.html
(3) After the "dark hour", the Australian trade minister was worried: willing to contact https://www.163.com/dy/article/G9C879AV053732N6.html with China
(4) China has a full fire! Australia 751.4 billion " taps are turned off, Australia Business: China must be respected
https://new.qq.com/omn/20210510/20210510A0648M00.html
(5) Australia Announces Announcement on Imported Food Monitoring Projects
https://www.baidu.com/link? url=9PsJTtCKgrEwzH-4AawfDnL2c2i-5eu_FQrk2_nEwY08XP8ErV0GzBc4rzAXnWBM7jtybbuGxcuHSk6jnAaA_a&wd= & eqid=d865c07200027df50000000560994070
- The Chinese Embassy and Consulate in Australia
Commonwealth Embassy in Australia
Ambassador: Cheng Jingye)
Address: 15 Coronation Drive,Yarralumla,ACT 2600,AUSTRALIA
National area Number: 0061-2
Tel.: 62283999
Fax: 62283836
Website: http://au.china-embassy.org
http://au.chineseembassy.org
Email: chinaemb_au@mfa.gov.cn
Economic and Business Office of the Chinese Embassy in Australia
Address: 15 Coronation Drive,Yarralumla,ACT 2600,Australia
Tel: 0061 2 62283962 / 63 / 64 / 65 / 66 / 67
Fax: 0061 2 62283991
Email: au@mofcom.gov.cn Website: au.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in Adelaide (Australia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN ADELAIDE
Consul General: He Lanjing (female) (He Lanjing)
Tel: 0061-8-82688807
Fax: 0061-8-82688800
Website: http://adelaide.china-consulate.org
PO Box: chinaconsul_adelaide@mfa.gov.cn
The Chinese Consulate-General in Adelaide
Address: 110 Crittenden Road,Findon SA 5023
Tel: 0061 8 82688807
Fax: 0061 8 82688800
Email: ade@mofcom.gov.cn
Website: adelaide.china-consulate.org
Consulate General in Brisbane (Australia)
CONSULATE GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN BRISBANE
Consul-General: Xu Jie (Xu Jie)
Address: Level 9,79 Adelaide St.,Brisbane QLD 4000
Tel: 07-32106509
Fax: 07-32106517
Website: http://brisbane.china-consulate.org
http://brisbane.chineseconsulate.org
Chinese Consulate General in Brisbane
Address: Level 9,79 Adelaide St,Brisbane,QLD 4000
Tel: 0061 7 32113681
Fax: 0061 7 30030668
Email: Brisbane@mofcom.gov.cn Website: Brisbane.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in Perth, Australia, Australia,
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN PERTH
Consul-General: Long Dingbin (Long Dingbin)
Address: 45 Brown Steet,East Perth,W.A. 6004,Australia
National area Number: 0061-8
Tel: 92220333,92220305
Leading Overseas Chinese Affairs Group (Visa, Overseas Chinese Affairs): 92220300,92220321,92220302
Business Room: 92220311,92220310
Fax: 92216144
Website: http://perth.china-consulate.org
http://perth.chineseconsulate.org
Email: chinaconsul_per_au@mfa.gov.cn
chinacon@iinet.net.au
China Consulate General in Perth
Address: 45 Brown St,East Perth,WA 6004
Tel: 0061 8 92220310
Fax: 0061 8 92216144
Email: Perth@mofcom.gov.cn Website: Perth.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in Melbourne (Australia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN MELBOURNE
Consul General: Dragon Boat (Long Zhou)
Address: 75-77 IRVING ROAD,TOORAK,MELBOURNE,VICTORIA 3142
Tel: 00613-98220604 (Visa), 98246450 (Office)
Fax: 0061-3-98220606
Website: http://melbourne.china-consulate.org
http://melbourne.chineseconsulate.org
Email: chinaconsul_mel_au@mfa.gov.cn
- China Consulate General in Melbourne Business Room
Address: 75-77 Irving Road,Toorak,VIC 3142
Tel: 0061 3 98229415
Fax: 0061 3 98220329
Email: Melbourne@mofcom.gov.cn Website: Melbourne.mofcom.gov.cn
Consulate General in Sydney (Australia)
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN SYDNEY
Consul-General: Zhou Limin (Zhou Limin)
Address: 39 Dunblane Street,Camperdown,NSW 2050,Australia
Tel: 0061-2-859580020061-2-85958000 (recorded telephone)
Fax: 0061-2-85958021
Website: http://sydney.china-consulate.org
http://sydney.chineseconsulate.org
Email: webmaster@sydney.chineseconsulate.org
Chinese Consulate General in Sydney
Address: 68 George St,Redfern,NSW 2016
Tel: 0061 2 96987788
Fax: 0061 2 96987373
Email: Sydney@mofcom.gov.cn Website: Sydney.mofcom.gov.cn
- The Australian Embassy and Consulate in China
The Australian Embassy in China
Embassy of Australia
Office: No. 21, Dongzhimen Outer Street, Sanlitun
Chancery: No. 21, Dong Zhi Men Wai Da Jie, San Li Tun
Tel. (Tel): 51404111 (Embassy) 85328686 (Business Office) 51404424 (Visa Office)
Fax (Fax): 51404348 (Military Office) 51404211 (Office)
51404230 (Culture Department) 51404337 (Department of Education)
65324606 (Business Office) 51404281 (Research Office)
51404204 (Consular, Administration Office) 51404164 (Visa Office)
Australian Consulate General in Shenyang
Consulate General of Australia in Shenyang
Office: Floor 19, Building A, China Resources Building, No. 286 Youth Street, Heping District, Shenyang, Liaoning
(Temporary office place: Room 2604, Excellence Building, No. 10, Huigong Street, Shenhe District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province)
CHANCERY:19F,CR Building,286 Qingnian Street,Heping District,Shenyang,Liaoning Province
(Temporary Office:Room 2604,26F,L'AVENUE Zhuoyue Building,10 Huigong Street,Shenyang,Liaoning Province)
Tel., TEL, No.: 024-22788232
Fax, FAX: 024-22788280
Area: Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang
DISTRICT:Liaoning,Jilin,Heilongjiang
Australian Consulate General in Chengdu
Consulate General of Australia in Chengdu
Office: 27th Floor, Baiyang Building, No. 18, Dongyu Street, Jinjiang District, Chengdu, Sichuan Province
CHANCERY:27F,Square One,18 Dongyu Street,Jinjiang District,Chengdu,Sichuan Province
TEL: 028-62685200
Fax, FAX: 028-62685222
Area: Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan
DISTRICT:Sichuan,Chongqing,Guizhou,Yunnan
Australian Commonwealth Consulate General in Guangzhou
Consulate General of Australia in Guangzhou
Office: 12th Floor, Development Center, No. 3, Linjiang Avenue, Zhujiang New City, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province
CHANCERY:12F,Development Centre,3 Linjiang Da Dao,Zhujiang New City,Guangzhou,Guangdong Province
Tel., TEL, No.: 020-38140111
Fax, FAX: 020-38140112
Area: Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Fujian, Hunan
DISTRICT:Guangdong,Guangxi,Hainan,Fujian,Hunan
The Australian Consulate-General in Shanghai
Consulate General of Australia in Shanghai
Office: 22nd Floor, CITIC Taifu Plaza, No. 1168, Nanjing West Road, Shanghai
CHANCERY:22F,CITIC Square,1168 West Nanjing Road,Shanghai
Tel. (TEL): 021-22155200
Fax, FAX: 021-22155252
Leading Area: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei
DISTRICT:Shanghai,Zhejiang,Jiangsu,Anhui,Jiangxi,Hubei
- Business Association
Australian Trade and Investment Commission
Australian Trade and Investment Commission The Australian Trade and Investment Commission (Australian Trade Commission, Austrade,, the Australian Embassy and Consulate in China) is the official trade, education and investment development promotion agency of the Australian Government. Through our global network, assist Australian companies to successfully expand their international business, attract effective foreign direct investment in Australia and connect with quality education in Australia around the world.
The Australian Trade and Investment Commission has a large, nationwide branch in Australia and has more than 80 overseas offices and agencies overseas. ——, the largest network of foreign government in China, serves through eight offices across the country.
Services to Australian export Businesses
AFTA provides a comprehensive range of services to help Australian export companies establish and develop international businesses, our services including introductions to different markets worldwide, market opportunity information and advice on overseas expansion, and financial grants for export market development and promotion activities for these businesses.
Services provided to overseas investors
It works with other government and business sectors to provide foreign investors with information needed to invest or expand business in Australia; to connect investors with their respective industry and government sectors; and to advise investment regulations and government investment encouragement policies.
Services offered to foreign buyers
The ATC can help foreign buyers save them time by finding the right Australian suppliers, assisting them in visiting Australia for talks with suppliers, and introducing information on the latest products and services in Australia.
Australian Chinese Enterprise Association, Chamber of Commerce
(1) Australian General Chamber of ChamencaThe Australian General Chamber of Commerce (CCCA) is a joint organization of Chinese companies in Australia as a non-profit society founded in 2006. As of late 2017, there were 328 member units located in New South Wales, Victoria, Western Australia and Queensland. Member business involves energy, minerals, trade, finance, transportation, real estate, manufacturing, tourism, agriculture and other fields. Headquartered in Sydney, there are four chapters in Sydney, Melbourne, Perth and Brisbane with five specialized committees of Legal and Compliance, Aviation, Resources and Energy, Women Entrepreneurs, and Foreign Relations Committees. The purpose of the General Chamber of Commerce is to serve members, safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of members, promote the development of economic and trade relations and exchanges between enterprises, and play a bridge and link for the business development of members in Australia and China. The current president is Chen Huaiyu, regional president and general representative of Bank of China Australia.
Since its establishment, the General Chamber of Commerce and its branches have strengthened their service functions, innovated service forms, built three communication platforms: "government and enterprise", "enterprise" and "meeting" member ", and enhanced the communication and exchanges between Chinese enterprises and Chinese embassies (consular) museums in Australia, with the local government, between the chamber of commerce and member enterprises, and between member enterprises. In recent years, not only successfully assist to carry out the Chinese high delegation visit Australia series of activities, China and Australia free trade agreement signed and mediation, related reception and other large-scale activities, also actively participate in compiling the investment guide to Australia "Chinese enterprises in Australia" and other books, but also actively carry out the chamber of commerce activities, enhance the cohesion of the chamber of commerce, highly praised by all walks of life.
—— Headquarters / The General Chamber of Commerce:
Level 12,39-41 York Street,Sydney,NSW Australia 2000
Tel: 0061 2 8235 5925 / 0061 2 8299 8010
Fax: 0061 2 9262 1794
Email: ccca.au@bankofchina.com
—— Sydney Branch / Sydney Branch:
Level 12,39-41 York Street,Sydney,NSW Australia 2000
Tel: 0061 2 8235 5925 / 0061 2 8299 8010
—— Melbourne Branch / Melbourne Chapter:
Level 3,379 Collins Street,Melbourne,VIC Australia 3000
Tel: 0061 3 9618 5502
—— Perth Branch / Perth Branch:
Level 41,108 St Georges Terrace,Perth,WA Australia 6000
Tel: 0061 8 9338 5513
—— Brisbane Branch / Brisbane Branch:
G/F 307 Queen St,Brisbane,QLD Australia 4000
Tel: 0061 7 3221 3988
(2) China Industry and Commerce Commission China Industry and Commerce Commission ("Australian Chamber of Commerce", ACBC) is a membership based non-profit, non-governmental organization founded in 1973 with associations and seven branches in Australia in New South Wales, Northern Territory, Queensland, South Australia, Western Australia, Victoria and the Capital Region.
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
|||||
 微信小程序
微信小程序