EFL · National City (Malaysia)
- Basic framework section
1, Framework section: Country elements
Malaysian National Flag
Signature construction: Kuala Lumpur Oil Twin towers

[Country Name] Malaysia (Malaysia).
[area] 330345 sq.
[Malaysia (Malaysia)
[area] approximately 330,000 square kilometers.
[population] 32.75 million. Of these, 69.1% are Malay, 23% Chinese, 6.9% Indian, and 1.0% of other races. Malay is Chinese, general English, and Chinese is widely used. Islam is a state religion, and other religions include Buddhism, Hindu, and Christianity.
[Capital] Kuala Lumpur (Kuala Lumpur), with a population of 1,791,300.
[Head of State] Sultan Sultan AbdullahibniSultan Ahmad Shah, who ascended the throne on 24 January 2019.
[Important Festival] National Day: August 31; Eid: May 24.
[Brief] Located in Southeast Asia, the land is separated into the east and west by the South China Sea. West Ma lies in the south of the Malay Peninsula, bordering Thailand in the north, Singapore across the Johor Strait in the south, the South China Sea in the east and the Strait of Malacca in the west. East Horse is located in the northern part of Kalimantan, adjacent to Indonesia, the Philippines and Brunei. The total length of a national coastline is 4,192 km. It is a tropical rainforest climate. The average annual temperature is 22-28 ℃ and the coastal plain is 25-30 ℃.
At the beginning of AD, the Malay Peninsula had ancient countries such as Capricorn swing and Wolf tooth repair. The Kingdom of Manraa, centered on Malacca in the early 15th century, unified most of the Malay Peninsula. Since the 16th century, it was occupied by Portugal, the Netherlands and Great Britain. It was completely made a British colony in the early 20th century. Sarawak and Sabah were historically Brunei, and they became British protectors in 1888. During World War II, the Malay Peninsula, Sarawak and Sabah were captured by Japan. Great Britain resumed colonial rule after the war. The United Malaya state declared its independence on August 31,1957. On 16 September 1963, the United Malaya State of Malaya merged with Singapore, Sarawak and Sabah to form Malaysia (Singapore withdrew on 9 August 1965).
[Politics] Malaysia is a democratic federal state with a constitutional parliament, whose political system is inherited from the British Westminster system. Due to historical reasons, Sarawak Prefecture and Sabah have greater autonomy.
[Constitution] The Constitution of Malaya was promulgated in 1957 and continued after the founding of Malaysia in 1963, renamed the Constitution of the Federation of Malaysia and revised several times. The Constitution stipulates that the Supreme Head of State is the head of state, leader of Islam and commander of the armed forces, elected by the council of rulers for a term of five years. The Supreme Head of State has the supreme powers of legislative, judicial and administrative powers, as well as to appoint prime ministers and refuse to dissolve Congress. In March 1993, the Malaysian Assembly passed constitutional amendments removing privileges like legal immunity. The constitution was amended in May 1994 to provide that the Supreme Head of State must accept and perform official duties on a government recommendation. In January 2005, the Malaysian parliament again passed the constitutional revision case and decided to transfer the management of water supply affairs and cultural heritage to the central government.
[Parliament] The Malaysian constitution makes the state a constitutional parliamentary democracy for the monarchy. Congress is the supreme legislature, consisting of the House of Lords and the Commons. The House of Commons has 222 seats for a five-year term, eligible for re-election. The current Speaker Nazius Azha, served in September 2020. The House of Lords has 70 seats, with two elected by each of the 13 states and the remaining 44 appointed by the Supreme Council for three-year terms. The current Upper Speaker, Raffles Aden, took office in September 2020.
[Government] The Malaysian government has not established the post of deputy prime minister, replacing four senior ministers, making it clear that the four senior ministers will share their responsibilities when he is absent.
[Administrative divisions] The country is divided into 13 states and three federal jurisdictions. The thirteen states are Johor, Kedah, Kelantan, Malacca, Semelan, Pahang, Penang, Perak, Glass City, Selangor, Dengjia Building and Sabah, Sarawak. There are the capitals Kuala Lumpur, Butra again (Bucheng) and Namuan.
[Judiciary] The Supreme Court was established on January 1,1985. It was renamed the Federal Court in June 1994. There are Malaya Superior Court (for West Ma) and Boro State Superior Court (for East Ma), and the states have district courts and inference chambers. There are also special military courts and Islamic courts. Chief Justice Dato 'Tengku Maimun binti Tuan Mat, took office in May 2019, Malaysia' s first female Chief Justice. Attorney General EdrusHaren, appointed in March 2020.
[Economy] Before the 1970 s, the economy was dominated by agriculture and relied on the export of primary products. Since the 1970 s, the industrial structure has been continuously adjusted and vigorously promoted the export-oriented economy, and the electronics, manufacturing, construction and service industries have developed rapidly. At the same time, the "new economic policy" of the Malay ethnic and indigenous people, aiming to achieve the goal of eliminating poverty and restructuring society.
In 2020, the Malaysian main economic figures are as follows:
GDP: Rm 1342 billion Git
GDP Growth rate: -5.6%
GDP per capita: 40,989
Total import and export: R. 1777.2 billion
Foreign exchange reserves: US $ 104.2 billion
[Resources] Natural resources are rich. Rubber, palm oil and pepper top the world in production and exports. Once a major tin producer in the world, the output has decreased year by year in recent years. Malaysia has rich oil reserves, including iron, gold, tungsten, coal, bauxite, manganese and other minerals. Rich in tropical hardwood.
[Industries] The Government encourages a processing industry with mainly domestic raw materials, focusing on the development of electronics, automotive, steel, petrochemical and textiles. In 2018, MA manufacturing output at 283.3 billion.
[Mining] mainly mines tin, oil and gas. According to the 2017 edition of the BP World Energy Statistics Yearbook, Ma crude oil reserves are 3.6 billion barrels and natural gas reserves are 1200 billion cubic meters. In 2017, Malaysian oil produced 648,000 barrels per day and 6,904 million standard cubic feet daily.
[Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries] cultivated area of about 4.85 million hectares. Agriculture is mainly cash crops, mainly including oil brown, rubber, tropical fruit and other fruits. Food self-sufficiency rate is about 70%. Rich in tropical trees. Fishing is mainly offshore fishing, and in recent years deep-sea fishing and aquaculture have developed in recent years. In 2018, horse agricultural output was R 95.5 billion.
[Resources] Malaysia 's main agricultural products are palm oil, rubber, cocoa, wood and pepper. It is the world' s second largest producer and exporter of palm oil and related products, and the world's third largest natural exporter of rubber. As of 2015, Malaysia has had proven oil reserves of 500 million tons (about 3.6 billion barrels), ranking fifth in the Asia-Pacific region behind China, India, Vietnam and Australia and 27th in the world. As of 2015, Malaysia has had proven natural gas reserves of 1.2 trillion cubic meters, ranking fifth in the Asia-Pacific region. In 2015, the natural gas production was 68.2 billion cubic meters, including the domestic consumption of 39.8 billion cubic meters, accounting for 58.4% of the total production. Malaysian iron, gold, tungsten, coal, bauxite, manganese and other minerals are also rich.
[Industry] After Malaysia's independence in 1957, the manufacturing industry mainly used its own resources to develop processing and manufacturing. With the in-depth development of electronics, petroleum, machinery, steel, steel, chemical and automobile manufacturing industries, the traditional primary product processing industry has gradually declined, and the manufacturing industry has become the main driving force for the Malaysian national economy development. In recent years, the horse manufacturing industry has developed stable, but the proportion of GDP has decreased year by year. In 2017, the manufacturing output was RM 193.01 billion, up 3.4% year-on-year, or 24.5% of GDP. The export amount was RM 549.61 billion, up 5.7% year on year, or 76.4% of the total exports. Electronics, machinery, petroleum and chemical industry account for 25.9%, 10.8%, 9.3%, and 7.2%, respectively. Major export markets include ASEAN (30.8%), China (14.0%), EU (10.3%), United States (9.8%), Japan (6.1%), and Hong Kong (5.6%).
Malaysian palm oil committee data, in 2017,5.81 million hectares, up 1.3% year on year, and original palm oil production was 19.92 million tons, up 15% year on year. By the end of 2016, brown oil reserves were 1.667 million tons, a 36.7% year-on-year decrease. Malaysia 's brown oil production and exports are second only to Indonesia, the world' s second largest producer and exporter. According to Malaysian Rubber Commission, 740,000 tons and 1,095,000 tons, 40.3% from Thailand and 1,194,000 tons, of which 73.3% were exported to China.
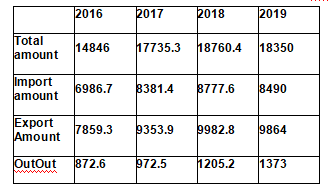
[Foreign Trade] According to the statistics of Malaysia Ministry of International Trade and Industry, in 2019, Malaysia's total foreign trade was RM 1.835 trillion, down 2.5% year on year, among which the export amount was RM 986.4 billion, RM 849.01 billion, and the trade surplus was 137.39 billion, which has achieved the trade surplus for 22 consecutive years since 1998. Despite the increased complexity of the international trade environment, Malaysian trade remains relatively stable, driven by export growth. In 2019, the main export markets were China, Singapore, United States and China, Singapore and United States.
Foreign trade in recent years is as follows (in Bilingjit):
[Major Trading Partner] According to the Malaysian Ministry of International Trade and Industry, in 2019, China, Singapore, the United States, Hong Kong, China and Japan, and the top five import sources were China, Singapore, the United States, Japan and Taiwan, China. China became the largest trading partner in Malaysia for the 11th consecutive year. According to Malaysian statistics, China and Malaysia accounted for 17.2% of the total Malaysian trade in 2019. In 2019, Malaysia was China's 9th largest trading partner and the 8th largest source of imports. It is China's second largest trading partner and the first largest source of import in ASEAN countries.
[Trade Structure] In 2019, the top five categories of Malaysian export products are electronic and electrical products, petroleum products, chemical and chemical products, palm oil and products, and LNG; the top five categories of import products are electronic and electrical products, chemical products, petroleum products, mechanical equipment and parts, and metal products.
[Bilateral Trade] China and Malaysia have signed more than 10 economic and trade cooperation agreements, including the avoidance of Double Tax Agreement, the Trade Agreement, the Investment Protection Agreement, the Maritime Transport Agreement and the Civil Air Transport Agreement. The Bilateral Economic and Trade Joint Commission was established in 1988. The Bilateral Business Council was established in April 2002. In 2017, the two countries signed the Memorandum of Understanding on Promoting Economic Development through the Chinese Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road Initiative, and the Memorandum of Understanding between the Chinese Ministry of Commerce and the Malaysian Ministry of Communications on Cooperation in the Field of Infrastructure Construction.
bilateral trade between Malaysia and China was RM 315.19 billion, up 0.2% in 2019, according to data released by the Malaysian Foreign Trade Development Authority. Among them, Malaysia's exports to China were RM 139.61 billion, up 0.3%; Malaysian imports from China were RM 175.59 billion, up 0.1%, or 20.7% of the total Malaysian imports. The Malaysian trade deficit was RM 35.98 billion, down RM 50 million from 2018.
In 2019, the growth of Malaysian exports to China mainly resulted from basic products, especially steel products,
LNG, pulp products, palm oil, metalwork, optical and scientific equipment, and processed foods. Palm oil exports to China rose 17.8% in 2019 after seven consecutive year declines. The growth of Malaysian imports from China is mainly petroleum products, transportation equipment and plastic products.
According to Chinese customs statistics, in 2019, bilateral trade between China and Malaysia reached USD 124 billion, up 14.2% year on year, China's exports to Malaysia were USD 52.13 billion, up 14.9% year on year, and imports from Malaysia reached USD 71.83 billion, up year-on-year of 13.6%.
China is Malaysia's largest trading partner, the largest source of import and the largest export destination. Bilateral trade has developed steadily. In recent years, the bilateral trade volume between China and Malaysia has maintained a scale of about $ 100 billion. According to China's statistics, the bilateral trade volume between China and Malaysia was US $ 131.16 billion in 2020, up 5.7% year on year; of which China exported US $ 56.43 billion and US $ 74.73 billion. China has become Malaysia's largest trading partner for 12 consecutive years. Main commodities imported from China include integrated circuits, computers and their parts, brown oil and plastic products; China exports main commodities include computers and their components, integrated circuits, clothing and textiles.
Literature and Art
After the independence of Malaya in 1957, the government promoted the Malay language and encouraged literary and artistic creation. Under the influence of the "Fifties faction", a new group of new writers appeared. Most of their works describe poverty in the lower society, imperialist slavery, and modern construction and racial integration. After 1958, the Malaysian Language and Book Bureau held a literary creation competition, which promoted the development of literary creation.
A Samad Said's novel Salina (1961) is an award-winning work, and its publication marks a new prosperity in contemporary Malaysian literature. The novel depicts the experience of a young girl becoming a prostitute insulted by a Japanese imperialism, exposing the evils caused by the imperialist war of aggression. The author was awarded the title "Literary Warriors" and won the ASEAN Literature Prize in Thailand in 1979. Shanen Akmard's novel "Full of Road Thorns" (1966) describes the painful experience of a family of nine farmers. His work won the award of literature, and the author also won the title of "Soldier of Literature". Other award-winning novels are Hasan Ali (1928~) 's "tramp" (1964), "Ring" (1965) by Areena Wati (1925~)' s "Hostage" (1971), "The Remote Village" (1964) "by Ibrahim Omar (1936~), Katija Hasim 's" White Pigeon Is Flying Again "(1972)," (1971) "by Abdullah ~' s" Chain " (1979) (1949~), and more.
Short stories from this period include 18 anthologies "Fight" (1968) "and 17 anthologies" Prize " (1972), bringing together 60 works from the late 1940 s to 1970 s, a collection of outstanding short stories after World War II. In poetry, the "hazy poetic school" appeared in the late 50 s, pursuing the beauty of formalism, and the obscure content, represented by Zachari (1930~), Nur (1933~), Amin (1929~) and others. The main force of poetry creation during this period were patriotic "fifties sect" poets such as Usman Awang, Masuri, and newly growing college poets such as Gassim, Ahhmad (1933~), Gemala (1941~), Wahab Ali (1941~), Kihati Abadi (1938~) and others. The works of college poets have made new developments in the subject matter. In the mid-1960 s, ─ ─, Radifer Merhedin, Baha Zain, who promoted the mold of any genre, and their poetry creation and literary ideas had some influence in the Malaysian poetry world after the 1970 s. Radiver Merhedin 's Mekong (1972), Baha Zain' s (1973), Muhammad Hagee Shalle's Travels II (1975) are all hits. The 1979 poetry collection, "The Times Bridge", gathers the works of famous Malaysian poets from the 1930 s to the 1970 s, with a distinct sense of The Times and ethnic characteristics.
Malaysian screenwriting, in the 1960 s, has developed from the traditional "Bonshawan" play to modern plays with realistic characteristics. "Wingroof and Roofs of Shae Leaves" (1963) by Galla Diwata (1925~) (1963), Usman Awan 's "From Stars to Stars" (1965), "Guests on the Kenny Hill" (1968), Galam Hamidi' s "Doom" was a representative play of this period. The historical drama "The Camel in Tanjung Bou" by playwright Saharom Hussein (1919~) is also an influential work in the Malaya region.
- Framework section: news hotspot
(1) Malaysia F&B flourished in Dubai Gore Foods in 2020
(2) MITI continues to create global champions under the Intermediate corporate development program through MATRADE
(3)Enhance Malaysia ' competitiveness in global markets during COVID-19 recovery
(4) Connect global businesses with # MYAPEC 2020 Exhibition
3, Framework Section: National · Human Geography
The area is 330,000 square kilometers. Located in Southeast Asia, located between the Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean. The whole territory is divided into the East Malaysia and Western Malaysia by the South China Sea. Western Malaysia is the Malaya region, located in the south of the Malay Peninsula, bordering Thailand in the north, the Strait of Malacca in the west, the South China Sea in the east, and East Malaysia is the Sarawak region and Sabah region, located in the north of Kalimantan Island. The Shoreline Minister is 4,192 km. It is a tropical rainforest climate. The average mountain temperature is 22 ℃ -28 ℃ and the coastal plain is 25 ℃ -30 ℃.
Malaysia is known as "the charm of Asia". The world-famous twin towers, high-rise commercial blocks and rubber gardens everywhere constitute a charming scenic painting. Although Malaysia is small, it is very strong, with its per capita annual income as high as $ 6,000. Malaysia has a total population of 32 million people, accounting for about 28%. It has a traditional Chinese culture for students to adapt to it. Currently 1.35 million people receive formal higher education, ranking among the best in Asia.
(1) The dances of all groups in Malaysia is always interesting and fascinating _ Bilibili
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av800549088? fromvsogou=1&bsource=sogou&fr=seo.bilibili.com
(2) Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Citscape iQIYI
https://www.iqiyi.com/v_198vsccuftc.html? fromvsogou=1 & fv=bf562ffc1cd15119
(3) First stop: Malaysia City View Watermelon Video
- Frame Section: Latest Information
(1) Malaysia F&B flourished in Dubai Gore Foods in 2020
(2) Malaysian high-quality durian products enter the Japanese market
(3) Enhance the Malaysian national brand through local catering products
(4) Malaysian food companies are allowed to import white sugar to gradually open up white sugar import in the future
https://finance.sina.com.cn/money/future/agri/2019-12-13/doc-iihnzhfz5737984.shtml
(5) Malaysia plans to amend its food regulations
http://news.foodmate.net/2021/04/590057.html
(6) General Provisions on Food Nutrition Labelling in Malaysia
http://news.foodmate.net/2020/11/577675.html
(7) Revised Microbiological Standards in Food in Malaysia
http://news.foodmate.net/2020/04/555903.html
(8) Malaysia plans to enter the global caviar market
http://news.foodmate.net/2019/09/534213.html
(9) Malaysian fish resources are at risk of depletion
http://news.foodmate.net/2018/12/496881.html
(10) Malaysian fish resources
http://news.foodmate.net/2018/12/496881.html
- Professional framework section
- Framework section: National · Food Introduction
[Agriculture and animal husbandry] Agriculture is mainly cash crops, mainly including oil brown, rubber, and tropical fruits. Food self-sufficiency rate is about 70%. In 2010, total agricultural output was 104.6 billion, accounting for 7.3% of gross national product and employment population of 1.475,000.
Rich in tropical trees. The fishery is mainly offshore fishing, with 526,000 tons in 2011.
In 2018, Malaysian agricultural output was RM 95.55 billion, down 0.4% year-on-year, or 7.8% of GDP. Malaysian agricultural products are mainly cash crops, mainly including palm oil, rubber, cocoa, rice, pepper, tobacco, pineapple, tea, etc.
6, Framework Section: Food Standards
(1) Malaysia revised new import requirements for grain and grain products
http://www.samr.gov.cn/gjhzs/jsxmycs/dt/202102/t20210209_326034.html
(2) Malaysia will strengthen food safety supervision over the export of China 's bird' s nest
http://www.ipraction.gov.cn/article/xwfb/gjxw/202004/153347.html
(3) Malaysia: The Bottle Import Guide
http://law.foodmate.net/show-191921.html
(4) Malaysia revised the amount of multiple pesticides in food
http://law.foodmate.net/show-203425.html
7, Framework Section: Policy and Regulations
7.1 Relevant Regulations on Malaysia Trade Management
7.1.1 Trade Authority
The Malaysian government department in charge of foreign trade is the Ministry of International Trade and Industry for developing investment, industrial development, and foreign trade policies, developing industrial development strategies, promoting bilateral trade cooperation, planning and coordinating the development of small and medium-sized enterprises, and promoting and enhancing the management and operational capacity of private business and indigenous communities.
7.1.2 Trade Regulatory System
Malaysia's main foreign trade laws are the Customs Law, Customs Import Control Regulations, Customs Export Control Regulations, Customs Valuation Regulations, Plant Quarantine Law, Protection of New Plant Variety Law, Anti-subsidy and Anti-dumping Law, Anti-subsidy and Anti-dumping Implementation Regulations, Guarantee Measures Law 2006, Foreign Exchange Administration Law, etc.
Relevant Provisions for 7.1.3 Trade Management
Malaysia has a free and open foreign trade policy, and the import and export of some commodities is subject to licensing or other restrictions
(I) Import management
In 1998, the Malaysian customs ban defined four categories of different levels.
The first category is 14 prohibited imports, including Chinese patent medicines containing ice tablets, accessory components, 45 plant drugs, and 13 animal and mineral drugs.
The second category is imported products that need licenses, mainly involving health, inspection and quarantine, safety, environmental protection and other fields. Includes poultry and beef (which must also be halal certified), eggs, rice, sugar, cement clinker, fireworks, audio and video tapes, explosives, wood, safety helmets, diamonds, rice mills, color copiers, some telecommunications equipment, weapons, arms, and saccharine.
The third category is temporary import restrictions, including milk, coffee, cereal powder, some wires and cables, and some steel products.
The fourth category is products that can be imported after meeting certain special conditions, including animals, animal products, plant and plant products, cigarettes, soil, animal fertilizer, bulletproof vests, electronic equipment, safety belts and imitation weapons.
In order to protect sensitive industries or strategic industries, Malaysia implements non-automatic import licensing management of some commodities, mainly involving the construction equipment, agriculture, mining and motor vehicle sectors. The importation of all heavy construction equipment shall be approved by the Ministry of International Trade and Industry and only subject to the inability of local Malaysian enterprises.
The Malaysian Ministry of International Trade and Industry and other departments are responsible for the issuance and day-to-day management of import licenses.
(II) Export management
Malaysia stipulates that most of the goods are freely exported to any country, except for Israel. However, some commodities are subject to export permission from government departments, including short items, sensitive or strategic or dangerous products, and wild protected species controlled or prohibited by national conventions.
Furthermore, the Malaysian Customs Order 1988 (No Export) provides for export management measures for three types of commodities:
The first category is the absolute ban on export, including the export of turtle eggs and vines; and prohibiting the export of oil, petroleum products and weapons and related products to Haiti;
The second category is the need of export license before export;
The third category is to export as necessary. Most of category II and III commodities are primary products such as livestock and their products, cereals, minerals / hazardous wastes; category III also includes weapons, arms, and antiques.
The Ministry of International Trade and Industry and the Ministry of Domestic Trade and Consumer Affairs are responsible for the management of export licenses for most commodities.
7.1.4 Inspection and Quarantine
Established in 2011, under the Ministry of Agriculture and Agricultural Products Industry, it is responsible for all ports of entry (including seaports, airports, land ports and mail and express delivery centers), quarantine stations, recommended facilities and issuing import and export licenses for plants, animals, frozen meat products, fish, agricultural products, soil and microbes.
In order to prevent the introduction of animal infectious diseases, animal parasitic diseases and plant dangerous diseases, insects, weeds and other pests, the government of Malaysia has conducted inspection and quarantine on imported animals and plants. If you bring animals and plants into the country, you should apply for an import license from the relevant Malaysian authorities in advance and observe the various inspection and quarantine procedures at the time of entry.
Malaysia requires that all meat, processed meat products, poultry meat, eggs and egg products must come from factories inspected and approved by the Ministry of Agriculture, and all imports must obtain import licenses issued by the Veterinary Services Bureau.
All meat, processed meat products, poultry meat, eggs and egg products supplied to Muslims must be halal certified and slaughterhouses for cattle, sheep and poultry and meat and egg processing equipment must be tested and approved by the Islamic Development Agency (JAKIM).
7.1.5 Customs Management Rules and Regulations
(I) Management organization
The Royal Malaysian Customs is the government department governing the import and export of goods, border control, and trade facilitation.
(II) Management system
There are two classification systems for Malaysian tariffs: one for internal ASEAN trade with a tax number of 6 digits and the other for trade with other countries. The Special Advisory Committee under the Ministry of International Trade and Industry reviews customs duties and publishes them annually in the government budget.
(III) Tariff level
Malaysian tariff 99.3% is ad valorem and 0.7% is from volume, mixed and selection tariffs. In 2016, the average tariff rate was about 5.8%, the average tariff for agricultural products was 8.4% and 5.4%, the World Trade Organization was 5.4%.
(4) Financial control
Whether Malaysian or non-resident, shall not exceed $ 10,000, whether Malaysian or non-resident, unlimited amount of foreign currency or traveler 's checks to Malaysia, but more than $ 10,000 to customs, foreign currency or traveler' s checks, including cash or prior written permission to the National Bank of Malaysia.
(V) Customs Room and Space Checklist
Recently, the Malaysian customs has revised the provisions on the customs cabin list, starting from 1 October 2018, which will require all goods imported and transferred from Malaysia, and the customer must provide the correct 6-bit cargo HS code for the goods description part in the sample list. Lack of HS CODE or incorrect information will affect the goods clearance in Malaysia and may cause customs fines or other liability consequences.
8, Framework Section: Exhibition Exhibition (Food)
(1) Kuala Lumpur Malaysia MIFB
https://www.qufair.com/convention/18355.shtml
Basic Information
Name: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia MIFB
Exhibition Date: 07.28 ~ 07.30,2021 Opening Time: 09: 00-18: 00
Venue: City: Malaysia-Kuala Lumpur-Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Host cycle: once a year
Exhibition Industry: Food, Beverage
Sponsor: Malaysia Expo International Company Limited
Exhibition area: 28,000
Number of square exhibitors: 1,300
Audience Number: 25,823 people
Industry properties
Food and beverage
Exhibit exhibits
Food Process Machinery Exhibition Area: Beverage, Food Retail Selling Machine Bottled Machine Catering Service Equipment Cleaning, Washing, Remaining Material Disposal Food Packaging Food Processing Equipment and Accessories Food Cooking Equipment and Parts Ice Cream / Ice Cream Machine Ice Maker Mapping Machine Packaging Material Refrigeration Equipment
General / comprehensive exhibition area: canned food; frozen food; condiments and sauces; desserts / chocolate / candy; dairy products; drinks-no alcohol; ingredients; fresh agricultural products; halal food healthy and organic food; vanilla and spices; and meat and poultry;; processing and convenient food; aquatic products
Special Specialty Exhibition Area: Coffee Modulations and Equipment Mixtures / Blender Coffee Bean Coffee Brewer Coffee Grinder Coffee Maker Coffee Baltenders, Sugar, Milk, Season and Syrup Coffee Oaster Tea Franchise Business Opportunities Barista Training
Aquatic products exhibition area: fresh aquatic products and seafood, frozen aquatic products, seafood processing products, after the processing and packaging of seafood, aquatic products processing and packaging equipment, logistics and transportation, aquatic industry service providers
Exhibition introduction
Since the establishment of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, MIFB in 1991, it is the largest, most professional and most well-known international food hotel exhibition in Malaysia. It has been successfully held for 14 sessions. The last FHM2017 exhibition attracted more than 1,300 exhibitors from 52 countries and regions, forming 13 countries and regional groups. During the four-day extension, 92% of exhibitors reached their goals and 91% confirmed that they will continue in 2019.25,823 professional visitors are mainly retailers from Malaysia and Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, India and others. The FHM is fully supported by the Malay government and DA, with relevant food and hotel seminars and chef performances.
Market Background
- Malaysia, one of the world's top 20.20 trading powers, is a major trading partner of China and India in the Asia-Pacific region. Main imported food: wheat, corn, sugar, rice, dairy products, fish, fruits, vegetables and meat; main exported food: livestock, fish, cereal products, tropical fruits. Malaysia is an emerging industrialized country with rich agricultural and mineral resources that can support its food processing and packaging industry, and the government encourages food factories, packaging companies and research institutes to cooperate in joint research on the development of food processing and packaging technologies.
- China 's food processing and packaging machinery is in Southeast Asian countries have a good market, especially in Malaysia, many Chinese companies have opened branches or agents, product sales momentum is good, Malaysia imported equipment amount above $ 10 billion, most of them from China, practice shows that Malaysia from scale, demand and market prospects analysis is China' s food processing, packaging machinery, expand the international market. According to the MIFB feedback of the Food and Beverage Exhibition in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, according to the Economic Secretariat of Malaysia, the bilateral imports and exports of Malaysia and China were US $ 777.7 in 2018, up 14.9%. Among them, Malaysia's exports to China were USD 34.41 billion, up 17.2%, making up 13.9% of total Malaysian exports, up 0.4 percentage points; US $ 43.36 billion, up 13.2%, or 20.0% of total imports from Malaysia, up 0.2 percentage points. The Malaysian trade deficit was $ 8.95 billion, the same period last year.
- Food Processing Exhibition and Food Packaging Exhibition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, PACK MALAYSIA
https://www.qufair.com/convention/14946.shtml
Basic Information
- Name: Name (Chinese): Food Processing Exhibition and Food Packaging Exhibition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, PACK MALAYSIA
Exhibition Date: July 15,2021-July 18,2021
Venue: Malaysia-Kuala Lumpur-Kuala Prince World Trade Center, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Exhibition cycle: once a year
Sponsor: Huaxun Exhibition Co., Ltd.
China Agency: Xiamen Wenxin Exhibition Co., Ltd
Industry properties
Exhibit exhibits
Food, Beverage, Alcohol, Tobacco, fresh
Exhibition introduction
Kuala Lumpur, International Printing, Packaging and Food Processing Exhibition, Malaysia PACK MALAYSIA is an influential international machinery exhibition in Southeast Asia. It has been successfully held for 25 sessions and has been recognized by the Joint Ministry of Foreign Trade in Malaysia.
The last exhibition has a total area of 18,000 square meters, and more than 200 companies from all over the world went to participate in the exhibition, about 920 stalls, with foreign exhibitors as high as 75%. During the exhibition, more than 39,000 professional trade audiences from all over Malaysian countries, Southeast Asia and the Middle East, and 85% of the exhibits were ordered on the spot. During the exhibition period, the Chinese exhibits were warmly welcomed by the buyers and achieved satisfactory exhibition results.
Malaysia is known as a transit trade country, transportation, political stability, plays a pivotal role in Southeast Asia and ASEAN, relatively close to West Asia, South Asia, Europe, America and the United States and Africa. In addition, close to the "Golden Waterway", the Channel of Malacca, gives Malaysia a unique transportation advantage.
Malaysia is a new industrialized country with rich agricultural and mineral capital that can support its food processing and packaging industry, and the government encourages food factories, baking eries, packaging companies and institutes to conduct research to develop food processing skills and packaging skills. In recent years in the world often affects the economy by rising market prices, Malaysia now turns its primary capital to processing manufacturing, including food processing, packaging industry and baking.
9, Framework Section: Food Category
In 2019, Malaysian agricultural output was RM 101.29 billion, up 1.8% year on year, or 7.1% of GDP. Malaysian agricultural products are mainly cash crops, mainly including palm oil, rubber, cocoa, rice, pepper, tobacco, pineapple, tea, etc.
- Framework section: Brand recommendation
Malaysia Shepherd Feng Biotechnology, Ltd. (Shepherd Feng has built a $ 7 million "water-soluble oil" processing plant in Malaysia.)
Sunhas invested $ 19.4 billion in China over the past five years. )
- Framework section: Enterprise recommendation
Cedami Limited
Sendami is the leading multinational group company in Malaysia. Its core business is not only in Malaysia, but also the forerunner of Malaysia towards globalization, but also the outstanding achievements in participating in China's modern industry. The investment of Sunami Group in China, whether in scale or industry, represents the focus of Malaysia's participation in development in China.
Sunami's business in China is mainly located in Shandong Province and the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Delta Energy and Public Utilities currently owns ports and tax businesses in Shandong Province, while Delta Industry also has business in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Over the past five years, it has invested $ 19.4 billion in China.
Malaysia Mufeng Shengke Co., Ltd
The employees of Malaysia Shepherd Biotechnology Co., Ltd. are committed to transforming creativity and technology into leading products and services, producing the most valuable green energy products, and doing their best to solve the current food safety crisis facing mankind! "Win-win alliance has integrity, happiness, health and safety, exporting innovative value, and assuming social responsibility" are the values that Mufeng Company has always followed. In order to provide Shepherd Feng's high-quality energy products to the vast world farmers, Shepherd Feng has built a $ 7 million "water-soluble oil" processing plant in Malaysia.
III. Professional Data
- Framework section: National · Food Data
(1) Announcement on allowing frozen durian imports in Malaysia
http://www.customs.gov.cn//customs/302249/302266/302267/2472801/index.html
(2) 1.111 tons! Xiamen Customs inspection and released the country's largest single Malaysian import of Mao Yan
http://www.customs.gov.cn//customs/xwfb34/302425/3206367/index.html
(4) Announcement of Customs No. 95 of 2019 (How to import Malaysian frozen durian)
http://www.customs.gov.cn//customs/302249/302270/302272/3267094/index.html
Statistical Table of China's Total Import and Export Commodities from Malaysia in the Recent Year
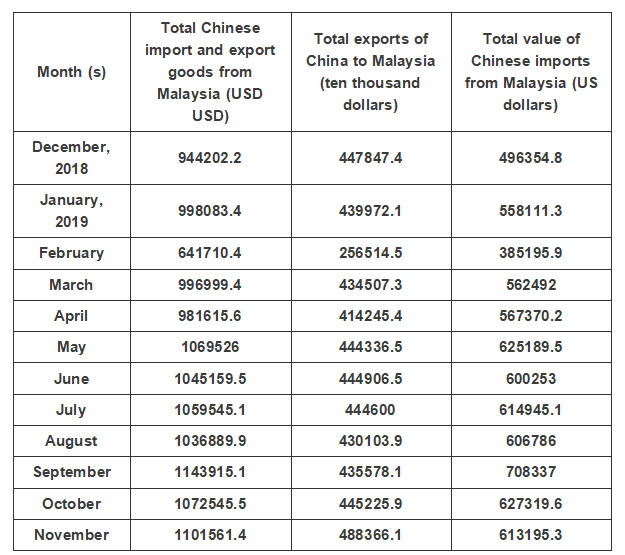
Data source: China Customs, organized by China Industry Research Institute
- The Chinese Embassy and Consulate in Malaysia
The Embassy in Malaysia
Ambassador: Ouyang Yujing (Ouyang Yujing)
Address: 229, JALAN AMPANG,50450 KUALA LUMPUR,MALAYSIA
Postal 50450
Visa Center: 00603-21760888
Tel.: 00603-21636853,00603-21645301
Consular Certificate: 00603-21645250
Political Office: Tel: 00603-21453936; Fax: 00603-21484495
Cultural Department: Tel: 00603-21416093; Fax: 00603-21429368
Business Office: Tel: 00603-42513555; Fax: 00603-42513233
Website: http://my.china-embassy.org/chn/
http://my.chineseembassy.org/chn/
Business Office of the Chinese Embassy in Malaysia
Address: NO. 39 Jalan Ulu Kelang,68000 Ampang,Selangor Darul Ehsan,Malaysia
Tel: 00603-42513555 Fax: 00603-42513233
Website: my.mofcom.gov. cn
- Consulate General in Penang (Malaysia)
- CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN PENANG
- Consul-General: Lu Shiwei (Lu Shiwei)
- Consulate-General Address: 28 B&C,Jalan Tunku Abdul Rahman 10350 George Town,Penang,Malaysia
- Tel: 0060-42189795
- Fax: 0060-42189798
- Chinese Citizen Guarantee and Assistance Tel: 0060-111059 2308
- Email: consulate_penang@mfa.gov.cn
- Website: http://penang.china-consulate.org/chn/
- http://penang.chineseconsulate.org/chn/
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN KOTA KINABALU
Consul-General: Liang (Liang Caide)
Address: Palm Court,Lot 7,No 3,VIP Lot,Lorong Pokok Palma Rajah,Jalan Lintas,88000 Kota Kinabalu,Sabah,Malaysia
Website: http://kotakinabalu.china-consulate.org/chn/(Chinese)
http://kotakinabalu.chineseconsulate.org/chn/(Chinese)
http://kotakinabalu.china-consulate.org/eng/(English)
http://kotakinabalu.chineseconsulate.org/eng/(English)
Tel: 0060-88385481
Fax: 0060-88385491
Chinese citizen Tel: 0060-149857312
Email: chinaconsul_kk_my@mfa.gov.cn
chinese_consulate_kk@yahoo.com
CONSULATE-GENERAL OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN KUCHING
Consul-General: Cheng Guangzhong (Cheng Guangzhong)
Address: No. 276, Section 10, Wangchang Waterway, Gujin City, Sarawak State, Malaysia
Lot 276,Block 10,Jalan Ong Tiang Swee,93200 Kuching,Sarawak,Malaysia
Tel: 006-082-240344
Fax: 006-082-232344
Website: http://kuching.chineseconsulate.org
Email: consulate_kuching@mfa.gov.cn
- Malaysian Embassy and Consulate in China
The Malaysian Embassy in China
Embassy of Malaysia
Office: No. 2 North Street, Chaoyang District: 100600
Chancery: No. 2, Liang Ma Qiao Bei Jie, Chaoyang District
Tel. (Tel): 65322531-200
Fax, Fax: 65325032
Email: Email (E-mail):mwbeijing@kln.gov.my)
Business Office: Unit E, Floor 11, Block B, Jiacheng Square
Tel., Tel: 84515109 84515113
Fax, Fax: 84515112
Email: Email (E-mail):beijing@matrade.gov.my)
Cultural Tourism Office: Room 506, Floor 5, Air China Building, 36 Xiaoyun Road
Tel: 84475056
Fax, Fax: 84475798
Investment Office: Unit C, Floor 12, Block A, Jiacheng Square
Tel. (Tel): 84400071 84400072
Fax (Fax): 84400776
Economic Office of the Malaysian Embassy in China
Address: No. 2, North Street, Liangmaqiao Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing
Tel: 010-65327990
Fax: 010-65323617
Consulate General of Malaysia in Xi ' an
Consulate General of Malaysia in Xi'an
Office: Unit 2, Floor 12, East Tower, Kaide Square, No. 64, West Section, Second Ring Road, Yanta District, Xi ' an, Shaanxi
(Temporary office place: Unit 3,4, Floor 6, East Tower, Kaide Square, No. 64, West Section, Second Ring Road, Yanta District, Xi ' an, Shaanxi Province)
CHANCERY:Unit 2,12F,East Tower of Capitaland Office Tower,64 South Second Ring Road,Xi'an,Shaanxi Province
(Temporary Office:Unit 3&4,6F,East Tower of Capitaland Office Tower,64 South Second Ring Road,Xi'an,Shaanxi Province)
TEL: 029-89568478
Fax, FAX: 029-89326122
Area: Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia
DISTRICT:Shaanxi,Gansu,Ningxia
Malaysian Consulate General in Kunming
Consulate General of Malaysia in Kunming
Office: Room 1503, Building 15, Office Building, Dianchi Road, Kunming City, Yunnan Province
CHANCERY:Room 1503,4F,Tower B,South Asia Top City Building,Dianchi Road,Kunming,Yunnan Province
Tel: 0871-63165088
Fax: 0871-63113503
Area: Yunnan, Sichuan, Chongqing
DISTRICT:Yunnan,Sichuan,Chongqing
Malaysian Consulate General in Nanning
Consulate General of Malaysia in Nanning
Office: 45th Floor, Land King International Chamber of Commerce Center, No. 59, Jinhu Road, Nanning City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
CHANCERY:45F,International Chamber of Commerce Tower,59 Jinhu Road,Nanning,Guangxi
Tel., TEL, No.: 0771-5662562
Fax, FAX: 0771-5662582
Leading area: Guangxi, Guizhou
DISTRICT:Guangxi,Guizhou
Malaysian Consulate General in Guangzhou
Consulate General of Malaysia in Guangzhou
Office: Room 1915-1918, CITIC Plaza Commercial Building, No. 233, North Tianhe Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province
CHANCERY:Room 1915-18,CITIC Plaza Office Tower,233 Tianhe Bei Road,Guangzhou,Guangdong Province
Tel. (TEL): 020-38770765
Fax, FAX: 020-38770769
Area: Guangdong, Fujian, Hainan, Hunan, Jiangxi
DISTRICT:Guangdong,Fujian,Hainan,Hunan,Jiangxi
The Malaysian Consulate-General in Shanghai
Consulate General of Malaysia in Shanghai
Office: Room 901, Building B, B, yin Building, No. 500 Ruby Road, Shanghai, postcode: 201103
CHANCERY:Room 901,Block B,Dawning Center,500 Hongbaoshi Road,Shanghai
Tel., TEL, No.: 021-60900360
Fax, FAX: 021-60900371
Area: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui
DISTRICT:Shanghai,Zhejiang,Jiangsu,Anhui
- Economic and Trade Organization (Embassy and Consulate)
Malaysian Chamber of Commerce and Societies:
- Chinese Great Hall of Malaysia
The Federation of Chinese Associations Malaysia
Address: No. 1 Jalan Maharajalela, 50150 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-22734008 Fax: 00603-22734015
Website: www.huazong.my
- Malaysia China General Chamber of Commerce
The Associated Chinese Chambers of Commerce and Industry of Malaysia (ACCCIM)
Address: 6th Floor,Wisma Chinese Chamber,258 Jalan Ampang,50450 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-42603090,42603091 Fax: 00603-42603080
Website: www.acccim.org. my
- Malaysia China General Chamber of Commerce
Malaysia-China Chamber of Commerce
Address: No. 8-2, Jalan Metro Pudu, Fraser Business Park, Off Jalan Yew, 55100 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-92231188 Fax: 00603-92221548
Website: www.mccc.my
- Malaysia-China Friendship Association
Malaysia-China Friendship Association (PPMC)
Address: Lot 10&11,13th Floor,Sun Complex,Jalan Bukit Bintang,55100 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-21416885 Fax: 00603-21411406
Website: www.ppmc.com. my
- China Business Council
Malaysia-China Business Council (MCBC)
Address: Level6-05 & 6-06, Menara LGB, No.1, Jalan Wan Kadir, Taman Tan Dr. Ismail, 60000 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-77271948 Fax: 00603-77251396
Website: www.mcbc.com. my
- Asian Strategy and Leadership Institute
Asian Strategy and Leadership Institute (ASLI)
Address: 1718, Jalan Ledang,Off Jalan Duta,50480 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-20935393 Fax: 00603-20933078
Website: www.asli.com. my
- National Federation of Commerce
National Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Malaysia (NCCIM)
Address: Level 3,West Wing,Menara MATRADE,Jalan Khidmat Usaha off Jalan Duta,50480,Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-62049811 Fax: 00603-62049711
Website: www.nccim.org. my
- Malaysia SME Council
SMI Association of Malaysia
Address: 18-3, Jalan USJ 9/5T,Subang Business Centre,47620 Subang Jaya,Selangor D.E.
Tel: 00603-80245787 / 5737,603-80230685 Fax: 00603-80241737
Website: www.smisme.com
- Malaysia Manufacturers ' Federation
Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers (FMM)
Address: No.3, Persiaran Dagang, PJU 9, Bandar Sri Damansara, 52200 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-62867200
Fax: 00603-62741266 / 7288
Malaysia-China Business Council (MCBC)
Address: Level6-05 & 6-06, Menara LGB, No.1, Jalan Wan Kadir, Taman Tan Dr. Ismail, 60000 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-77271948 Fax: 00603-77251396
Website: www.mcbc.com. my
- Asian Strategy and Leadership Institute
Asian Strategy and Leadership Institute (ASLI)
Address: 1718, Jalan Ledang,Off Jalan Duta,50480 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-20935393 Fax: 00603-20933078
Website: www.asli.com. my
- National Federation of Commerce
National Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Malaysia (NCCIM)
Address: Level 3,West Wing,Menara MATRADE,Jalan Khidmat Usaha off Jalan Duta,50480,Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-62049811 Fax: 00603-62049711
Website: www.nccim.org. my
- Malaysia SME Council
SMI Association of Malaysia
Address: 18-3, Jalan USJ 9/5T,Subang Business Centre,47620 Subang Jaya,Selangor D.E.
Tel: 00603-80245787 / 5737,603-80230685 Fax: 00603-80241737
Website: www.smisme.com
- Malaysia Manufacturers ' Federation
Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers (FMM)
Address: No.3, Persiaran Dagang, PJU 9, Bandar Sri Damansara, 52200 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-62867200
Fax: 00603-62741266 / 7288
- The Malay Chamber of Commerce
Malay Chamber of Commerce (DPMM)
Address: No. 33 & 35, Jalan Medan Setia 1, Bukit Damansara, 50490 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-20962233 Fax: 00603-20962533
Website: www.dpmm.org. my
- Malay Workers of Association
Malay Businessmen & Industrialists Association of Malaysia (PERDASAMA)
Address: lot1717,Jalan Ledang Off Jalan Duta,50480 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-20952002
Website: www.perdasama.org. my
- Shirron Indian Chamber of Industry
Kuala Lumpur & Selangor Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (KLSICCI)
Address: No. 116,2nd Floor, Jalan Tuanku Abdul Rahman, 50100 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-26931033 Fax: 00603-26911670
Website: www.klsicci.com. my
- Indian Chamber of Industry and Industry
Malaysian Associated Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (MAICCI)
Address: JKR3190,Jalan Ledang,Off Jalan Duta,50480 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-20110478 Fax: 00603-20110477
Website: www.maicci.org. my
- Malaysia International Chamber of Commerce and Industry
Malaysian International Chamber of Commerce and Industry
Address: C-08-08,Plaza Mont'Kiara,2 Jalan Kiara,50480 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-62017708 Fax: 00603-62017705
Website: www.micci.com
- Malaysian Chinese Law Federation
Malaysian China Legal Cooperation Society
Address: 10 Persiaran Dagang,Bandar Sri Damansara,Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-61794259 Fax: 00603-62536311
Email: mclcs.acclaim@gmail.com
- General Chamber of Commerce of Chinese Enterprises, Malaysia
China Enterprises Chamber of Commerce in Malaysia (CECCM)
Address: Level 1,Bank of China (Malaysia) Berhad, Plaza OSK 25 Jalan Aampang, 50450 Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 00603-2387 8101
Fax: 00603-21644240
Email: cenam1449@gmail.com Website: www.ceccm.com. my
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
|||||
 微信小程序
微信小程序